Visual manufacturing opens the door to a fascinating realm where innovation meets efficiency. Dive into this dynamic field as we uncover the key aspects and real-world applications that make visual manufacturing a game-changer in the industry.
As we delve deeper, you'll gain insights into the tools, technologies, implementation strategies, and the transformative impact visual manufacturing has on modern production processes.
Definition of Visual Manufacturing

Visual Manufacturing is a methodology that utilizes visual aids and tools to streamline and enhance manufacturing processes. It focuses on using visual cues to communicate information effectively, improve workflow efficiency, and minimize errors in production.
Key Components of Visual Manufacturing
- Visual Work Instructions: Step-by-step instructions presented visually to guide operators through the manufacturing process.
- Visual Performance Metrics: Displaying key performance indicators and metrics in a visual format to track and monitor production performance.
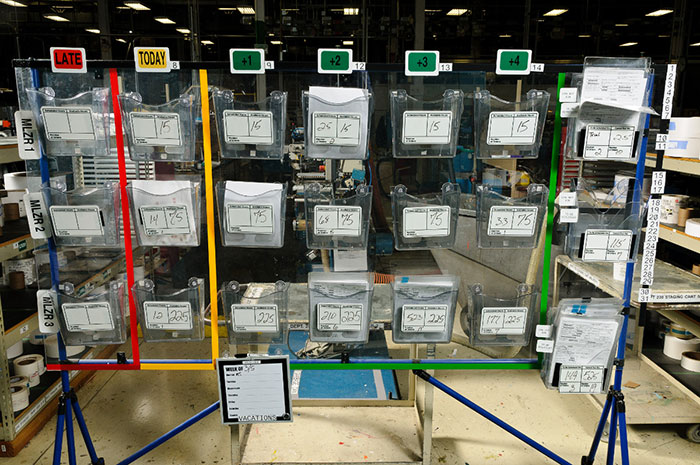
- Visual Inventory Management: Using visual signals like kanban cards to manage inventory levels and replenishment.
- Visual Factory Layout: Designing the layout of the manufacturing facility in a way that visually communicates the flow of materials and processes.
Examples of Visual Manufacturing in Industry
- Toyota Production System: Toyota pioneered the use of visual manufacturing techniques such as Andon lights to signal production issues and promote quick response.
- Lean Manufacturing: Lean principles incorporate visual tools like 5S (Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, Sustain) to optimize workspace organization and efficiency.
- Electronic Kanban Systems: Many manufacturing companies utilize electronic kanban systems to visually manage inventory levels and trigger replenishment orders automatically.
Benefits of Visual Manufacturing
Visual manufacturing offers a range of advantages for companies looking to streamline their production processes and improve efficiency.
Increased Productivity and Efficiency
- Visual manufacturing provides clear, easy-to-understand instructions for workers, reducing errors and minimizing downtime.
- By using visual cues, employees can quickly identify issues and address them promptly, leading to faster production cycles.
- Overall, this leads to increased productivity and efficiency in the manufacturing process.
Improved Quality Control
- Visual manufacturing allows for real-time monitoring of production processes, enabling immediate detection of defects or anomalies.
- By catching issues early on, companies can maintain high quality standards and reduce the risk of producing faulty products.
- This results in improved customer satisfaction and a stronger reputation in the market.
Cost Savings
- With the reduction in errors and defects, companies can save on costs associated with rework, scrap, and warranty claims.
- Visual manufacturing also helps optimize resource utilization, leading to lower operational expenses.
- Overall, implementing visual manufacturing can result in significant cost savings for companies in the long run.
Real-Life Success Stories
Companies like Toyota and Boeing have successfully implemented visual manufacturing principles in their production facilities, leading to significant improvements in efficiency, quality, and cost savings.
For example, Toyota's use of visual management techniques in its factories has helped the company achieve high levels of productivity and quality, making it a leader in the automotive industry.
Similarly, Boeing has utilized visual manufacturing methods to streamline its aircraft assembly processes, resulting in faster production cycles and reduced lead times.
Tools and Technologies for Visual Manufacturing

Visual manufacturing relies on a variety of tools and technologies to streamline processes, improve efficiency, and enhance decision-making. By leveraging the power of IoT (Internet of Things) and AI (Artificial Intelligence), manufacturers can achieve greater visibility, control, and optimization throughout the production cycle.
Tools Used in Visual Manufacturing
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): These technologies allow manufacturers to visualize and simulate production processes, identify potential issues, and train employees in a virtual environment.
- RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification): RFID tags enable real-time tracking of raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods, providing valuable insights into inventory levels and production status.
- Machine Vision Systems: Using cameras and sensors, machine vision systems inspect products for defects, monitor assembly processes, and ensure quality control.
How Technology Enhances Visual Manufacturing Processes
- IoT: Connected devices and sensors collect data from machines, equipment, and systems, enabling real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and performance optimization.
- AI: Artificial Intelligence algorithms analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns, predict outcomes, and optimize production schedules, leading to improved efficiency and cost savings.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud platforms provide secure storage, remote access, and collaboration tools, allowing manufacturers to centralize data, streamline communication, and enable real-time decision-making.
Software Applications Tailored for Visual Manufacturing
- FactoryLogix: This MES (Manufacturing Execution System) software integrates production data, quality management, and process control, offering real-time visibility into operations and enabling continuous improvement.
- Simio: A simulation software that helps manufacturers optimize production workflows, layout designs, and resource utilization, reducing lead times and minimizing bottlenecks.
- PTC Vuforia: An AR platform that enables manufacturers to create interactive work instructions, remote assistance tools, and digital twins for enhanced training, maintenance, and troubleshooting.
Implementation of Visual Manufacturing
Implementing visual manufacturing into an existing production setup requires a strategic approach to ensure a smooth transition and maximum efficiency. Training employees to adopt visual manufacturing practices is crucial for the successful implementation of this system. Challenges may arise during the implementation phase, but with proper planning and solutions, these obstacles can be overcome effectively.
Steps for Integrating Visual Manufacturing
- Assess Current Processes: Analyze the existing production setup to identify areas where visual manufacturing can be implemented for improved efficiency.
- Develop a Plan: Create a detailed implementation plan outlining the steps, timeline, and resources required for integrating visual manufacturing.
- Training and Education: Provide comprehensive training to employees on the principles and practices of visual manufacturing to ensure a smooth transition.
- Implement Visual Tools: Introduce visual tools such as Kanban boards, Andon lights, and visual work instructions to enhance visibility and communication on the shop floor.
- Monitor and Evaluate: Continuously monitor the implementation progress and evaluate the effectiveness of visual manufacturing practices to make necessary adjustments.
Training Required for Employees
- Basic Principles: Educate employees on the basic principles of visual manufacturing, including visual controls, standardized work, and continuous improvement.
- Hands-On Training: Provide hands-on training sessions to allow employees to practice using visual tools and techniques in real-world scenarios.
- Feedback Mechanism: Establish a feedback mechanism for employees to share their experiences, suggestions, and challenges related to visual manufacturing.
Common Challenges and Solutions
- Resistance to Change: Address employee resistance by clearly communicating the benefits of visual manufacturing and involving them in the implementation process.
- Lack of Understanding: Offer additional training and support to employees who may have difficulty grasping the concepts of visual manufacturing.
- Resource Constraints: Allocate sufficient resources, including time, budget, and manpower, to ensure a successful implementation of visual manufacturing.
Final Thoughts
As we conclude our exploration, visual manufacturing emerges as a pivotal force reshaping the manufacturing landscape, paving the way for streamlined operations and enhanced productivity. Dive into this visual revolution and unlock new possibilities for your business.
Helpful Answers
What is visual manufacturing?
Visual manufacturing is a methodology that utilizes visual aids and tools to streamline production processes and enhance operational efficiency.
How does visual manufacturing differ from traditional methods?
Visual manufacturing emphasizes visual communication and management techniques, offering a more intuitive and efficient approach compared to conventional methods.
What are some common challenges during the implementation of visual manufacturing?
Common challenges include resistance to change, inadequate training, and integration issues with existing systems. Overcoming these hurdles requires proper planning and stakeholder engagement.