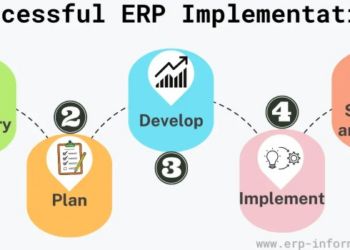
Embarking on a successful ERP implementation journey requires a meticulous blend of key components and strategic planning. Dive into this engaging exploration to uncover the essentials of a seamless ERP system integration.
Key Components of a Successful ERP Implementation
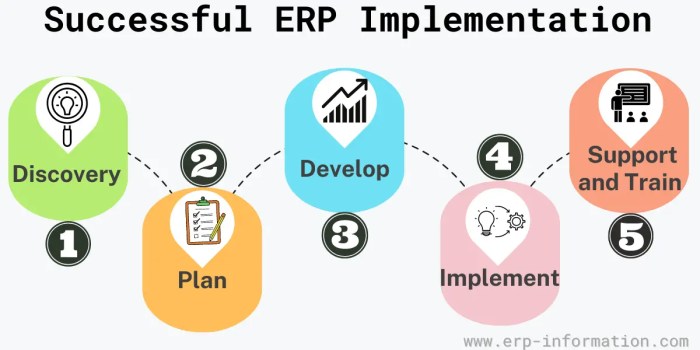
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) implementation is a complex process that requires careful planning and execution. Several key components play a crucial role in ensuring the success of an ERP implementation. Each component has its significance and interacts with others to streamline processes and achieve the desired outcomes.
Comprehensive Needs Assessment
A comprehensive needs assessment is the foundation of a successful ERP implementation. This component involves evaluating the existing systems, processes, and workflows within an organization to identify areas that need improvement. By conducting a thorough needs assessment, businesses can determine their specific requirements and goals, which will guide the selection and customization of the ERP system.
Effective Change Management Strategy
Change management is essential for overcoming resistance to change and ensuring a smooth transition to the new ERP system. An effective change management strategy involves clear communication, training programs, and support mechanisms to help employees adapt to new processes and technologies.
By addressing employee concerns and providing adequate support, businesses can minimize disruptions and maximize the benefits of the ERP implementation.
Robust Data Migration Plan
Data migration is a critical component of ERP implementation, as it involves transferring data from existing systems to the new ERP platform. A robust data migration plan ensures the accurate and secure transfer of data, minimizing the risk of data loss or corruption.
By carefully mapping data sources, cleansing data, and testing migration processes, businesses can prevent potential issues and maintain data integrity throughout the implementation process.
Customization and Configuration
Customization and configuration of the ERP system are essential to align the software with the unique requirements of the business. This component involves tailoring the system to meet specific business processes, industry standards, and regulatory requirements. By customizing and configuring the ERP system effectively, businesses can optimize workflows, improve efficiency, and enhance overall performance.
Ongoing Support and Maintenance
Post-implementation support and maintenance are crucial for the long-term success of an ERP system. This component involves providing continuous support, troubleshooting issues, and implementing updates to ensure the ERP system remains functional and aligned with the evolving needs of the business.
By investing in ongoing support and maintenance, businesses can maximize the ROI of their ERP system and drive continuous improvement.
Importance of Comprehensive Planning
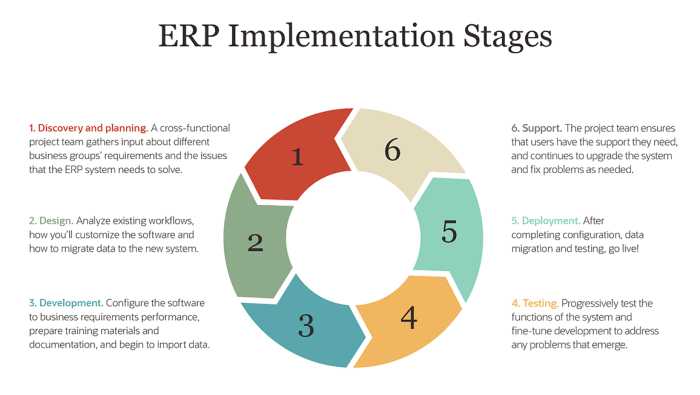
Effective planning is crucial before implementing an ERP system as it sets the foundation for a successful implementation. Thorough planning helps in identifying potential challenges, allocating resources efficiently, and ensuring that the project stays on track. Without comprehensive planning, the ERP implementation process can be chaotic and prone to failure.
Key Planning Activities for Successful Implementation
- Defining clear objectives and goals: Establishing specific objectives and goals helps in aligning the ERP implementation with the organization's strategic vision.
- Conducting a thorough needs assessment: Understanding the current processes, pain points, and requirements of the organization is essential for selecting the right ERP solution.
- Creating a detailed project plan: Developing a well-structured project plan with clear timelines, milestones, and responsibilities ensures that the implementation stays on schedule.
- Training and change management: Planning for training sessions and change management activities is crucial to prepare employees for the new system and minimize resistance to change.
How Detailed Planning Mitigates Risks
- Identifying and addressing potential roadblocks: Through detailed planning, organizations can anticipate challenges and develop contingency plans to mitigate risks during the implementation phase.
- Resource allocation and budget management: Comprehensive planning helps in allocating resources effectively and managing the budget efficiently, reducing the chances of cost overruns.
- Ensuring stakeholder alignment: Involving key stakeholders in the planning process fosters alignment and commitment, increasing the likelihood of a successful ERP implementation.
Role of Stakeholder Engagement
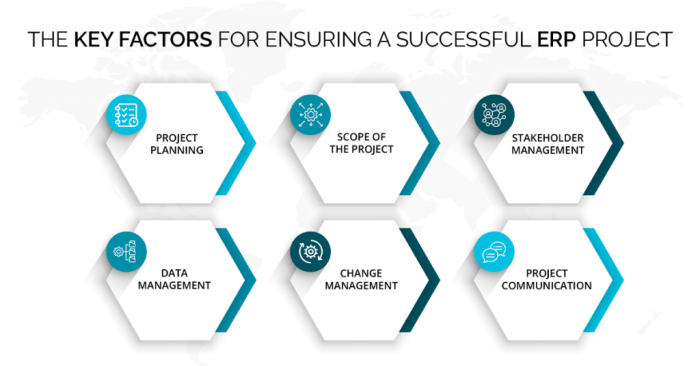
Engaging stakeholders throughout the ERP implementation process is crucial for the success of the project. Stakeholders are individuals or groups that have a vested interest in the outcome of the implementation, such as employees, managers, customers, and suppliers. Their involvement can greatly impact the overall success and adoption of the ERP system.
Importance of Engaging Stakeholders
Effective communication and collaboration with stakeholders are essential to ensure that their needs and concerns are addressed during the implementation. By involving stakeholders from the beginning, you can gain valuable insights, feedback, and buy-in, which can help in shaping the project's direction and ensuring its alignment with organizational goals.
- Regular updates and transparent communication: Keeping stakeholders informed about the progress, challenges, and decisions made during the implementation process can help in managing expectations and building trust.
- Seeking feedback and input: Encouraging stakeholders to provide feedback, suggestions, and concerns can lead to a more tailored and successful implementation that meets their requirements.
- Training and support: Providing adequate training and support to stakeholders can increase their confidence and willingness to embrace the new ERP system.
- Addressing resistance: Identifying and addressing any resistance or concerns from stakeholders early on can prevent roadblocks and ensure a smoother implementation process.
Stakeholder engagement is not just about informing them of the changes but actively involving them in the decision-making process and seeking their input to ensure a successful ERP implementation. Their involvement can lead to higher user adoption rates, increased satisfaction, and ultimately, the successful realization of the project goals.
Data Migration Strategies
When implementing an ERP system, one of the critical aspects to consider is data migration. This process involves transferring data from old systems to the new ERP system. There are several data migration strategies commonly used in ERP implementations, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
Full Migration
Full migration involves transferring all existing data from the legacy systems to the new ERP system. This approach ensures that all historical data is available in the new system, providing a complete view of the organization's operations. However, full migration can be time-consuming and costly, especially if the data is outdated or redundant.
Partial Migration
Partial migration focuses on transferring only essential data to the new ERP system. This approach helps streamline the migration process by excluding unnecessary or obsolete data. While partial migration is quicker and more cost-effective than full migration, there is a risk of losing valuable historical data that may be needed for analysis or compliance purposes.
Phased Migration
Phased migration involves dividing the data migration process into stages or phases. This approach allows organizations to prioritize data sets based on their criticality and complexity. By migrating data in phases, organizations can minimize disruption to daily operations and address any issues that may arise gradually.
However, phased migration requires careful planning and coordination to ensure a smooth transition between phases.
Parallel Migration
Parallel migration involves running the new ERP system alongside the existing legacy systems for a certain period. During this time, data is simultaneously entered and processed in both systems to ensure accuracy and consistency. Once the new system is validated, the legacy systems are phased out.
While parallel migration minimizes the risk of data loss and disruption, it can be resource-intensive and complex to manage.
Best Practices for Data Migration
- Conduct a thorough data assessment to identify and categorize data based on relevance and quality.
- Develop a detailed data migration plan with clear objectives, timelines, and responsibilities.
- Test data migration processes in a controlled environment to identify and resolve any issues before full implementation.
- Ensure data integrity by validating and reconciling migrated data with source systems.
- Provide training and support to end-users to facilitate the adoption of the new ERP system.
Training and Change Management
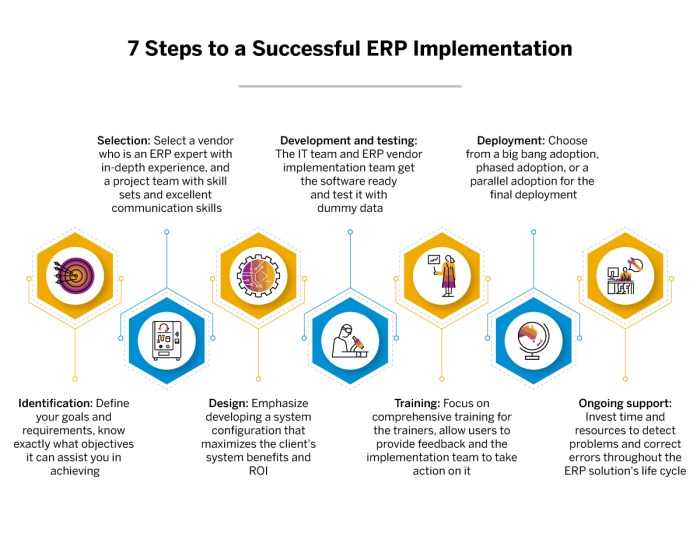
Training programs play a crucial role in the successful implementation of an ERP system. They help end-users and staff understand the new processes, functionalities, and tools that come with the ERP software. Training ensures that employees are equipped with the necessary skills to effectively use the system, leading to increased productivity and efficiency.Change management is equally important during an ERP implementation as it helps organizations overcome resistance to new processes and technologies.
It involves preparing employees for the changes, addressing their concerns, and guiding them through the transition. By effectively managing change, organizations can minimize disruptions and ensure a smooth adoption of the ERP system.
Successful Training and Change Management Strategies
- Provide hands-on training sessions tailored to different user groups to ensure they understand how to use the ERP system in their specific roles.
- Offer ongoing support and refresher training to address any challenges or questions that may arise after the initial implementation.
- Engage key stakeholders early in the process to gain their buy-in and support for the changes brought about by the ERP system.
- Communicate transparently about the reasons for implementing the ERP system and the benefits it will bring to the organization and its employees.
- Implement a feedback mechanism to gather input from end-users and address any issues or concerns promptly.
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, mastering the art of successful ERP implementation hinges on a synergy of meticulous planning, stakeholder engagement, data migration finesse, and effective training strategies. Let this comprehensive guide empower your ERP endeavors towards lasting success.
Questions and Answers
What are the most common data migration strategies in ERP implementations?
Common data migration strategies include direct data transfer, data mapping, and API integration.
How does stakeholder engagement influence the success of an ERP implementation project?
Stakeholder engagement ensures alignment of goals, fosters communication, and secures buy-in for the project, crucial for success.
Why is change management important during ERP implementation?
Change management helps in preparing employees for new processes, addressing resistance, and ensuring a smoother transition.