Kicking off with erp financial systems, this opening paragraph is designed to captivate and engage the readers, providing a comprehensive overview of ERP systems in the financial realm. From understanding the significance of ERP to exploring popular examples and key features, this intro sets the stage for an informative discussion ahead.
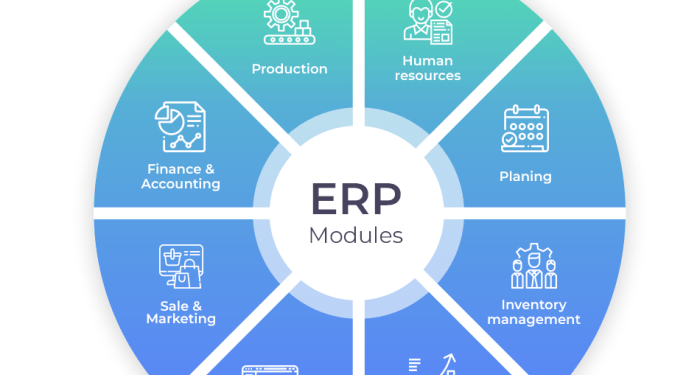
Overview of ERP Financial Systems
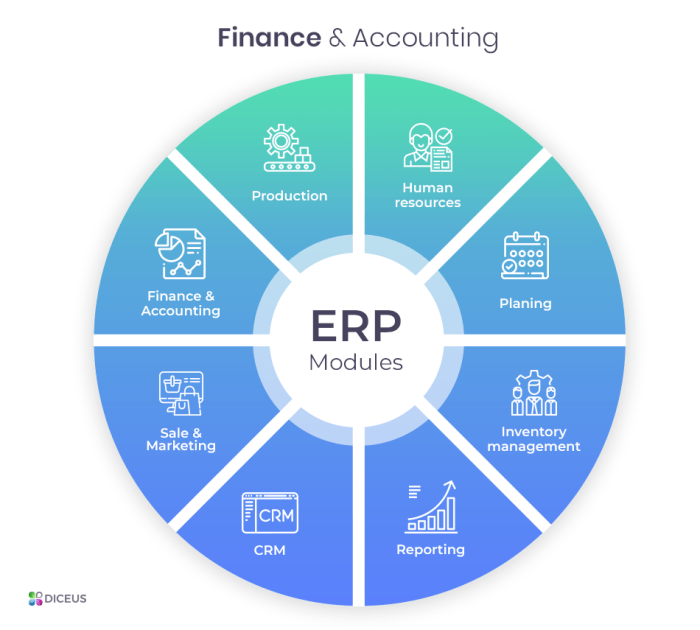
ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning, and it plays a crucial role in integrating various business processes, including financial management, into a single system. ERP financial systems help organizations streamline their financial operations, enhance decision-making, and improve overall efficiency.
Popular ERP Systems for Financial Management
- Oracle NetSuite: Known for its cloud-based financial management capabilities, Oracle NetSuite offers features such as financial planning, billing, and revenue recognition.
- SAP S/4HANA: SAP S/4HANA is a leading ERP system that provides real-time financial insights, automated financial processes, and advanced analytics for better decision-making.
- Dynamics 365 Finance: Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance offers comprehensive financial management solutions, including budgeting, financial reporting, and cash flow optimization.
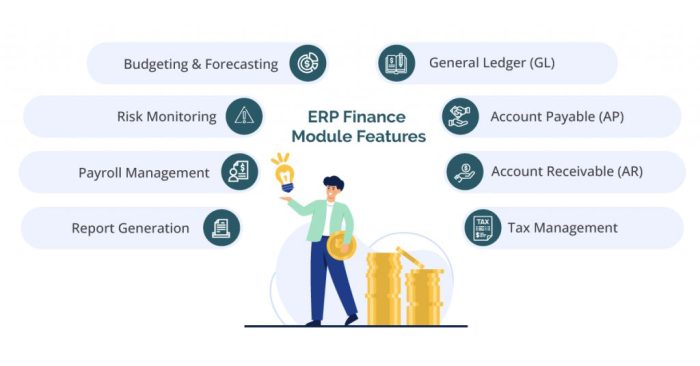
Primary Features and Functions of ERP Financial Systems
- Financial Planning and Analysis: ERP financial systems enable organizations to create budgets, forecast financial performance, and analyze financial data for strategic planning.
- Financial Reporting: These systems generate detailed financial reports, statements, and dashboards to provide insights into the financial health of the organization.
- Accounts Payable and Receivable: ERP systems automate processes related to accounts payable and accounts receivable, including invoice processing, payment management, and credit control.
- Asset Management: ERP financial systems help track and manage assets, depreciation, and maintenance schedules to optimize asset utilization and reduce costs.
- Compliance and Risk Management: These systems ensure compliance with financial regulations, internal controls, and risk management practices to mitigate financial risks and ensure transparency.
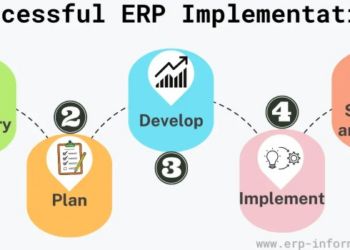
Implementation of ERP Financial Systems
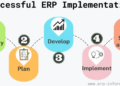
Implementing ERP financial systems is a complex process that requires careful planning and execution. Below are the steps involved in implementing ERP financial systems, along with the challenges organizations may face and best practices for a successful implementation.
Steps in Implementing ERP Financial Systems
- 1. Planning: Define the objectives, scope, and timeline of the implementation process.
- 2. Selection: Choose the right ERP system that aligns with your organization's needs and goals.
- 3. Configuration: Customize the ERP system to meet your specific financial requirements.
- 4. Data Migration: Transfer data from existing systems to the new ERP system accurately and securely.
- 5. Testing: Conduct rigorous testing to ensure the ERP system functions as intended.
- 6. Training: Provide comprehensive training to employees to ensure they can effectively use the ERP system.
- 7. Go-Live: Transition to the new ERP system gradually to minimize disruptions to operations.
- 8. Support: Offer ongoing support and maintenance to address any issues that arise post-implementation.
Challenges in ERP System Implementation
- - Resistance to Change: Employees may resist adopting new processes and technologies.
- - Integration Issues: Ensuring seamless integration with existing systems can be challenging.
- - Data Security Concerns: Protecting sensitive financial data from breaches and cyber threats.
- - Cost Overruns: Budget constraints and unexpected expenses can derail the implementation process.
Best Practices for Successful ERP Financial System Implementation
- - Executive Sponsorship: Secure buy-in from top management to drive the implementation process.
- - Cross-Functional Team: Involve stakeholders from different departments to ensure a comprehensive approach.
- - Change Management: Implement strategies to address resistance and promote employee adoption.
- - Continuous Communication: Keep all stakeholders informed and engaged throughout the process.
- - Regular Evaluation: Monitor progress, identify issues early, and make necessary adjustments.
Integration with Existing Systems

Integrating ERP financial systems with other existing systems is crucial for ensuring seamless operations and maximizing efficiency within an organization.
Common Integration Points
There are several common integration points between ERP systems and other software solutions:
- Integration with CRM systems to streamline customer data and improve sales forecasting.
- Integration with HR systems for better management of payroll, employee data, and performance tracking.
- Integration with supply chain management systems to optimize inventory levels and enhance procurement processes.
- Integration with business intelligence tools for real-time reporting and data analysis.
Benefits of Seamless Integration
Seamless integration of ERP financial systems with existing systems offers numerous benefits for overall business operations:
- Enhanced data accuracy and consistency across different departments.
- Improved decision-making through access to real-time information and analytics.
- Increased productivity by eliminating manual data entry and redundant processes.
- Cost savings by avoiding the need for multiple standalone systems and reducing maintenance expenses.
Customization and Configuration
Customization and configuration are essential aspects of implementing ERP financial systems to ensure they meet specific business requirements and function effectively. Let's delve into the process of customizing ERP financial systems, the available configuration options, and the pros and cons of each approach.
Customizing ERP Financial Systems
Customizing ERP financial systems involves tailoring the software to align with the unique needs and processes of a particular business. This may include modifying workflows, adding new features, or integrating third-party applications to enhance functionality. The process typically requires collaboration between the ERP vendor and the organization to understand requirements and make necessary adjustments.
- Customization allows businesses to address specific challenges and optimize processes to improve efficiency.
- It enables organizations to differentiate themselves by creating a system that aligns perfectly with their operations.
- However, customization can be time-consuming, costly, and may lead to complexities during upgrades or maintenance.
Configuration Options in ERP Systems
ERP systems offer a range of configuration options that allow users to tailor the software without altering its core code. These options typically include setting up chart of accounts, defining approval workflows, configuring reporting structures, and adjusting security settings. Configuration can be done through user-friendly interfaces provided by the ERP software.
- Configuration provides flexibility to adapt the ERP system to specific business needs without the need for extensive coding.
- It simplifies the implementation process and ensures compatibility with future updates and enhancements.
- However, configuration may have limitations in meeting highly specialized requirements that may necessitate customization.
Pros and Cons of Customization vs. Configuration
When deciding between customization and configuration in ERP implementations, organizations must weigh the advantages and disadvantages of each approach. Customization offers a tailored solution but comes with added complexity and maintenance costs. On the other hand, configuration provides flexibility and ease of implementation but may not address all unique business requirements.
- Customization can deliver a competitive edge and streamline processes but requires a significant investment of time and resources.
- Configuration offers quick implementation and adaptability but may not fully meet specialized needs without customization.
- Organizations should carefully evaluate their requirements and consider the long-term implications of customization versus configuration in their ERP financial systems.
Last Word
In conclusion, ERP financial systems play a crucial role in streamlining financial management processes for organizations. From successful implementation to seamless integration with existing systems, the benefits are vast. This outro encapsulates the essence of ERP financial systems and their impact on modern businesses.
Key Questions Answered
What does ERP stand for?
ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning, a software system that integrates various functions across a business into one comprehensive platform.
What are some popular ERP systems used for financial management?
Popular ERP systems for financial management include SAP, Oracle Financials, Microsoft Dynamics, and NetSuite.
What are the challenges organizations may face during ERP system implementation?
Challenges during ERP implementation may include data migration issues, resistance from employees, and the need for extensive training.
What are the benefits of seamless integration for overall business operations?
Seamless integration of ERP systems with existing software leads to improved data accuracy, streamlined processes, and enhanced decision-making capabilities.
What is the difference between customization and configuration in ERP systems?
Customization involves modifying the software to meet specific business needs, while configuration uses existing tools to tailor the system without changing its core code.