EP ERP sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality. From understanding the concept to exploring integration with other business systems, this guide delves deep into the world of EP ERP with a focus on clarity and insight.
Understanding EP ERP
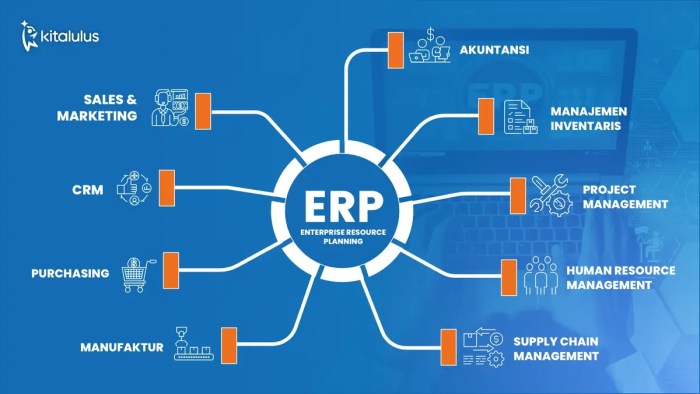
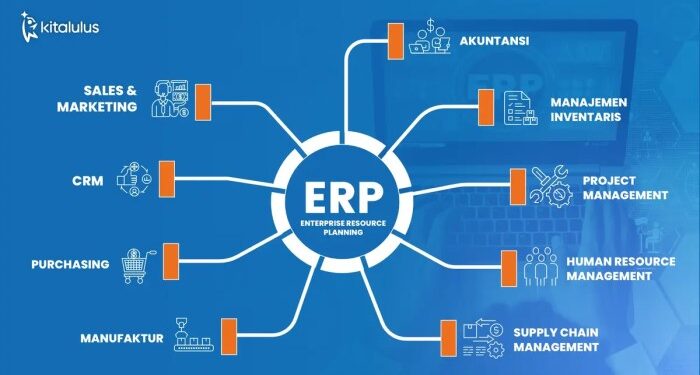
EP ERP, or Enterprise Performance Enterprise Resource Planning, is a software system that integrates the main functional areas of an organization to streamline processes and information across the company. It helps in automating business processes and centralizing data, making it easier for decision-makers to have a comprehensive view of the organization's performance.
Key Components of EP ERP
- Financial Management: Includes modules for accounting, budgeting, and financial planning.
- Supply Chain Management: Manages procurement, inventory, and logistics processes.
- Human Resources: Handles employee information, payroll, and benefits administration.
- Customer Relationship Management: Focuses on managing customer interactions and sales processes.
- Business Intelligence: Provides tools for data analysis and reporting to support decision-making.
Benefits of Implementing EP ERP
- Improved Efficiency: EP ERP helps in automating processes, reducing manual tasks, and increasing productivity.
- Enhanced Visibility: By centralizing data, EP ERP provides real-time insights into the organization's performance, enabling better decision-making.
- Cost Savings: Streamlining processes and reducing errors can lead to cost savings in the long run.
- Scalability: EP ERP systems are designed to grow with the organization, accommodating changes and expansions easily.
- Compliance: Helps in ensuring regulatory compliance and maintaining data security standards.
Types of EP ERP Systems
When it comes to EP ERP systems, there are different types available to cater to the diverse needs of businesses. Let's explore the various types to understand their differences and applications.
On-Premise vs. Cloud-Based EP ERP Systems
On-premise EP ERP systems are installed and managed on the company's own servers and infrastructure, providing complete control over data and customization. On the other hand, cloud-based EP ERP systems are hosted on remote servers and accessed through the internet, offering scalability, flexibility, and reduced maintenance costs.
Open-Source vs. Proprietary EP ERP Systems
Open-source EP ERP systems provide access to the source code, allowing for customization and community support. In contrast, proprietary EP ERP systems are developed and owned by a specific vendor, offering unique features, dedicated support, and security measures.
Scalability of EP ERP Systems
EP ERP systems vary in their scalability to accommodate the needs of small, medium, and large enterprises. Small businesses may opt for basic features and modules to start with, while medium-sized enterprises may require more advanced functionalities. Large enterprises typically require robust and scalable EP ERP systems to manage complex operations and high volumes of data efficiently.
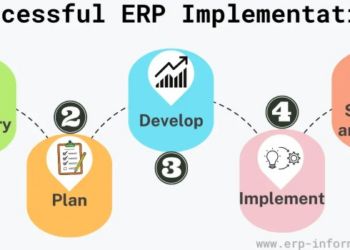
Implementation of EP ERP
Implementing an EP ERP system in an organization involves several key steps to ensure a successful integration and adoption across various departments.
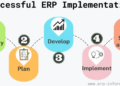
Steps for Successful EP ERP Implementation
- Establish clear goals and objectives for the ERP implementation.
- Conduct a thorough analysis of current business processes and identify areas for improvement.
- Choose the right EP ERP system that aligns with the organization's needs and requirements.
- Develop a detailed implementation plan with timelines, milestones, and responsibilities clearly defined.
- Provide adequate training and support to employees to ensure they are comfortable using the new system.
Best Practices for a Successful EP ERP Implementation
- Engage key stakeholders from different departments throughout the implementation process.
- Allocate sufficient resources, both in terms of budget and manpower, for the implementation.
- Regularly communicate progress and updates to all employees to ensure transparency and alignment.
- Conduct thorough testing and quality assurance to identify and address any issues before full deployment.
- Monitor and evaluate the system post-implementation to measure performance and identify areas for further improvement.
Challenges and Risks in EP ERP Implementation
- Resistance to change from employees accustomed to existing processes.
- Data migration issues leading to loss of important information.
- Integration challenges with existing systems and software in the organization.
- Potential disruption to daily operations during the transition period.
- Risk of project delays and cost overruns if not managed effectively.
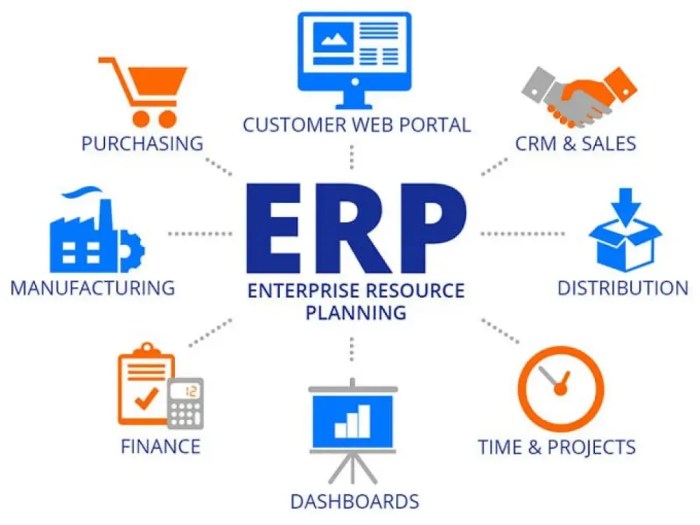
Integration with other Business Systems
When it comes to Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, integration with other business systems is crucial for maximizing efficiency and productivity. Let's delve into how EP ERP systems integrate with Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems, the importance of integrating EP ERP with supply chain management systems, and the role of business intelligence tools in enhancing the functionality of EP ERP systems.
Integration with CRM Systems
Integrating EP ERP systems with CRM systems allows for seamless communication and data sharing between sales, marketing, and customer service departments. This integration enables businesses to have a 360-degree view of their customers, leading to improved customer satisfaction and retention.
By syncing customer data, order information, and sales history between ERP and CRM systems, organizations can streamline processes and provide personalized service to customers.
Importance of Integrating EP ERP with Supply Chain Management Systems
The integration of EP ERP with supply chain management systems is essential for optimizing inventory management, procurement, and logistics operations. By connecting these systems, businesses can achieve real-time visibility into their supply chain, track shipments, manage vendor relationships, and ensure timely delivery of products to customers.
This integration enhances efficiency, reduces costs, and minimizes disruptions in the supply chain, ultimately improving overall business performance.
Role of Business Intelligence Tools in Enhancing EP ERP Systems
Business intelligence tools play a vital role in enhancing the functionality of EP ERP systems by providing actionable insights and data analytics. These tools enable organizations to analyze trends, forecast demand, identify opportunities for growth, and make informed decisions based on data-driven insights.
By integrating business intelligence tools with EP ERP systems, businesses can optimize operations, improve decision-making processes, and drive strategic planning for long-term success.
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, EP ERP emerges as a transformative tool for businesses of all sizes, promising efficiency, integration, and enhanced decision-making capabilities. As organizations navigate the complexities of implementing and integrating EP ERP systems, the potential for growth and success becomes more tangible than ever before.
Essential FAQs
What are the key components of EP ERP?
The key components of EP ERP typically include modules for finance, human resources, supply chain management, and customer relationship management.
What is the difference between on-premise and cloud-based EP ERP systems?
On-premise EP ERP systems are installed locally on a company's hardware and servers, while cloud-based systems are hosted remotely and accessed online.
How can organizations mitigate challenges during EP ERP implementation?
Organizations can mitigate challenges by conducting thorough training, involving key stakeholders, and ensuring proper data migration strategies are in place.